

|
It is the atmospheric layer where sun radiation is strong enough to
make electrons escape from atoms (ionization process).
For this reason this zone strongly interacts with electromagnetic waves, that can be absorbed, deviated or reflected. This is a problem for the scientists who would like an atmosphere transparent at all frequencies (astronomers and radio-astronomers), but this is also the fact that make possibile long distance radio contacts. There are four layers of interest in the ionosphere, and they are named D, E, F1 and F2. |
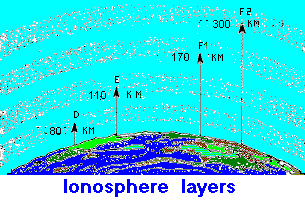
|
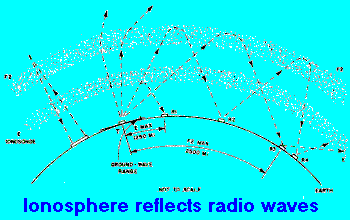
| Guglielmo Marconi demonstrated first that radio waves can go well beyond the horizon, reaching very distant sites. A radio signal can be reflected by the ionosphere and bounce back to the earth surface, thousand of miles away. Moreover, since the earth itself, and particularly the ocean, can reflect radio waves, multiple ionosphere hops become possibile, and the signal can travel up to antipodes. |
|
The probability of a useful reflexion is related to the frequency of the
radio signal and the ionization level.
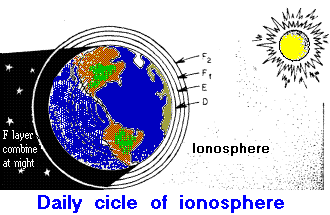
The ionization changes according to the sunspot number and to the solar radiation flux, which has a 11 years cycle and is also influenced by the season and the hour of the day. The frequencies affected by this propagation mode are those below about 50 MHz. On upper frequencies the ionospheric propagation is absolutely rare, except when there is an extremely ionizated layer, sporadic E), which is temporary and unforecastable. |